Our lab has a rich history on the development of fast MRI techniques that acquire less k-space data (undersampling) and reconstruct images without undersampling errors by exploiting image properties, such as compressibility, structure, similarity to other images, etc. Previous work was based on compressed sensing to exploit the natural compressibility of medical images to reduce k-space data and accelerate acquisition. Current work is focused on deep learning, where a reconstruction network is learned from multiple examples to map undersampled k-space data to images without undersampling errors. Our AI reconstruction work evolved from supervised to self-supervised learning and from image-to-image mapping to generative networks.
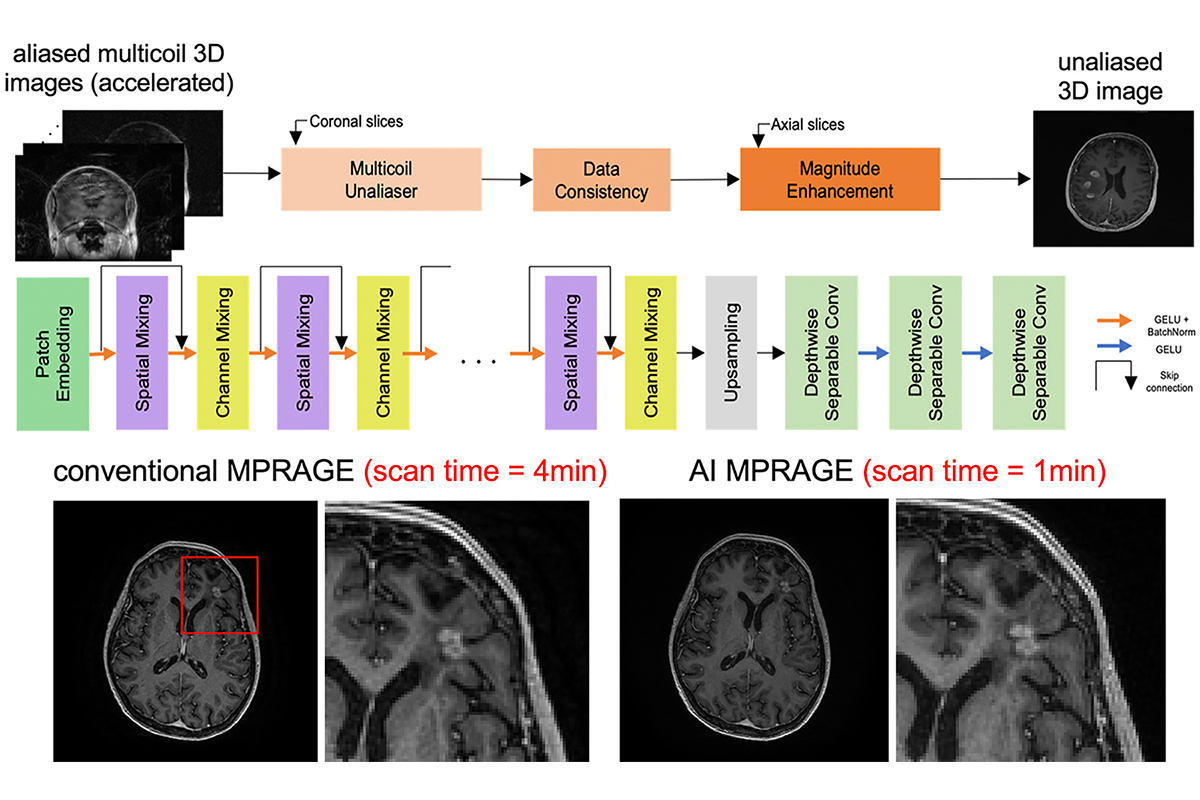
- High acceleration of 3D brain MRI using modular networks: Figure 1 for an example of 8-fold acceleration of brain MPRAGE to reduce the scan time to only 1 minute.
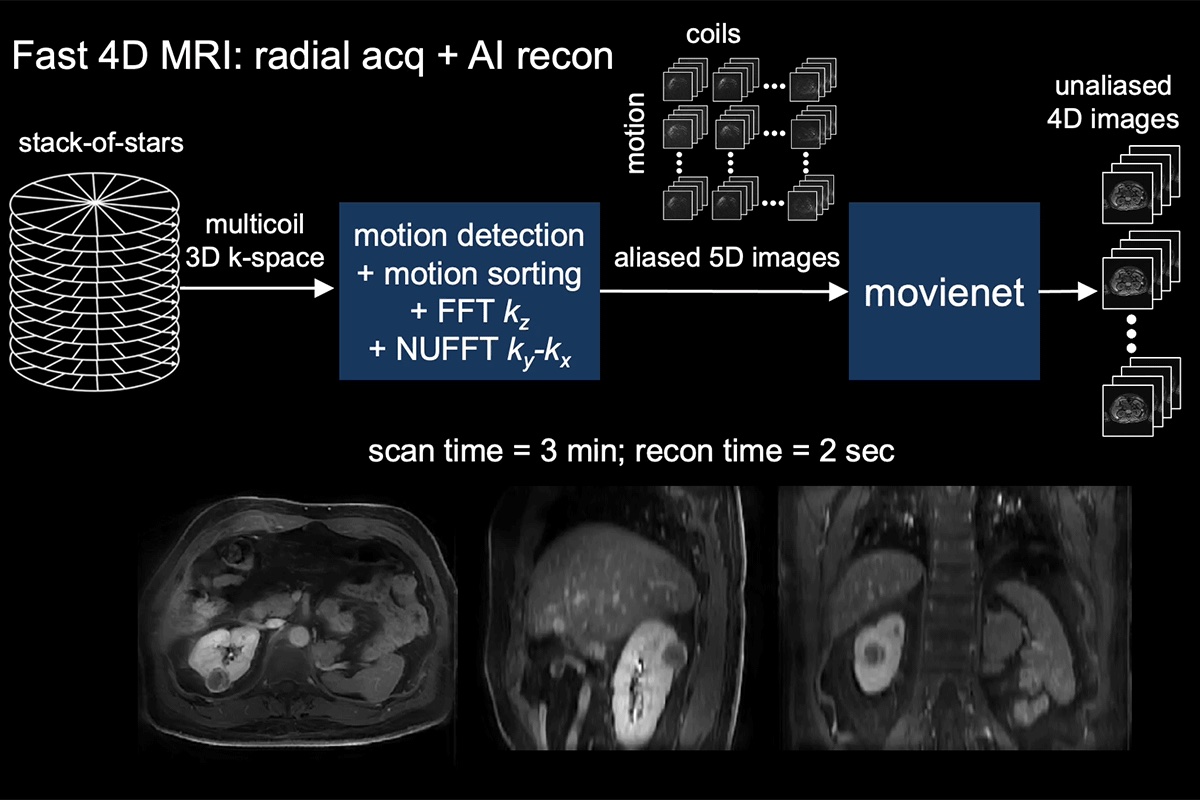
- Movienet reconstruction network for dynamic motion-resolved 4D MRI: not only to reduce scan time but to significantly reduce the reconstruction time and enable 4D MRI in a clinical setting – see Figure 2 for an example of Movienet which replaces k-space consistency for motion consistency to reduce the reconstruction time to less than 1 second (compressed sensing 4D MRI reconstruction time was higher than 10 minutes).
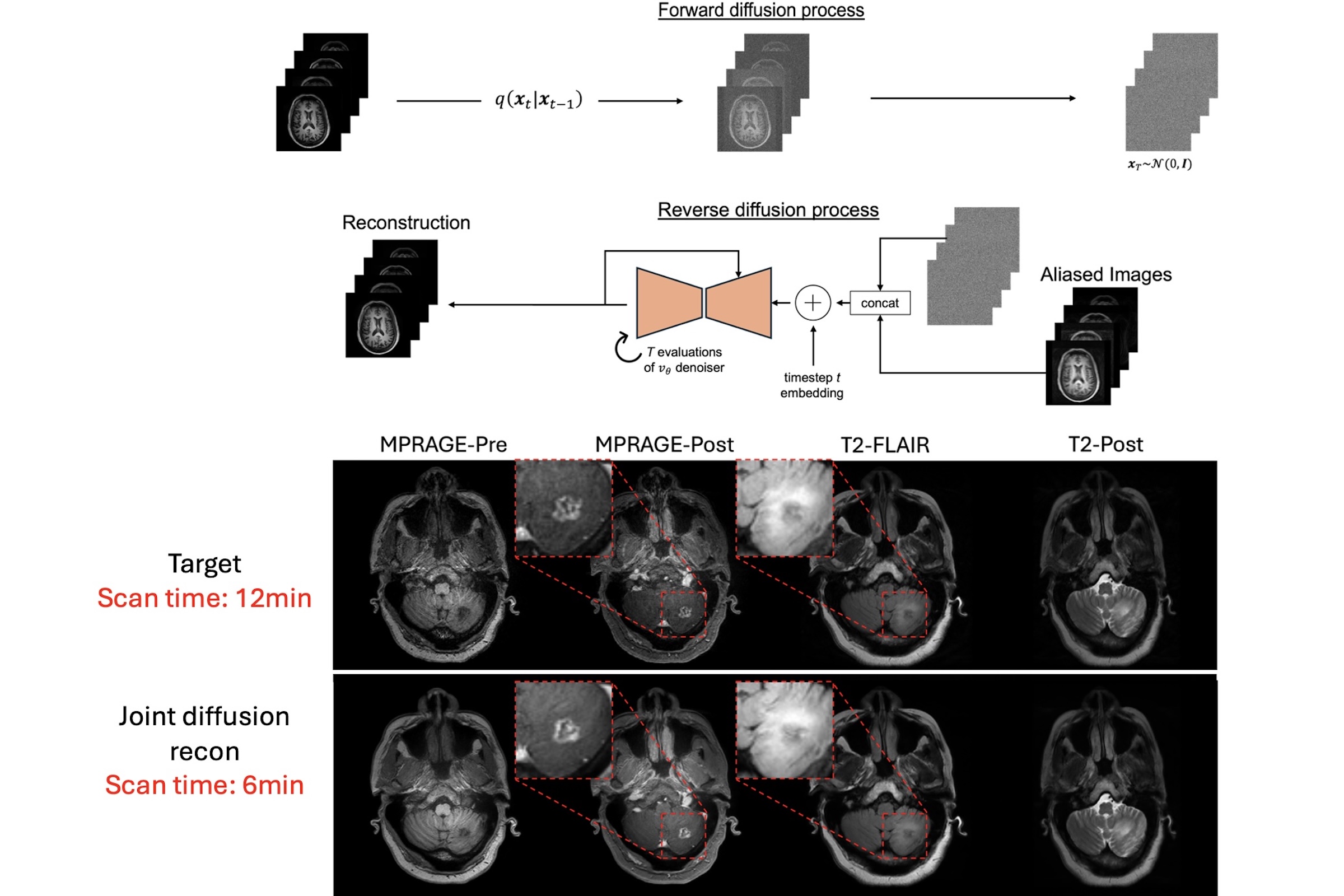
- Generative diffusion AI-based reconstruction for multi-sequence acceleration of brain imaging: joint acceleration of 4 sequences (MPRAGE-Pre, MPRAGE-Post, T2-FLAIR, and T2-Post) was performed using a diffusion network that learns a common image distribution model and generates images without aliasing artifacts from under sampled k-space data. Figure 3 shows the diffusion network workflow and application to a scan a patient with brain tumors in only 6 minutes, with comparable image quality to the standard scan of 12 minutes.
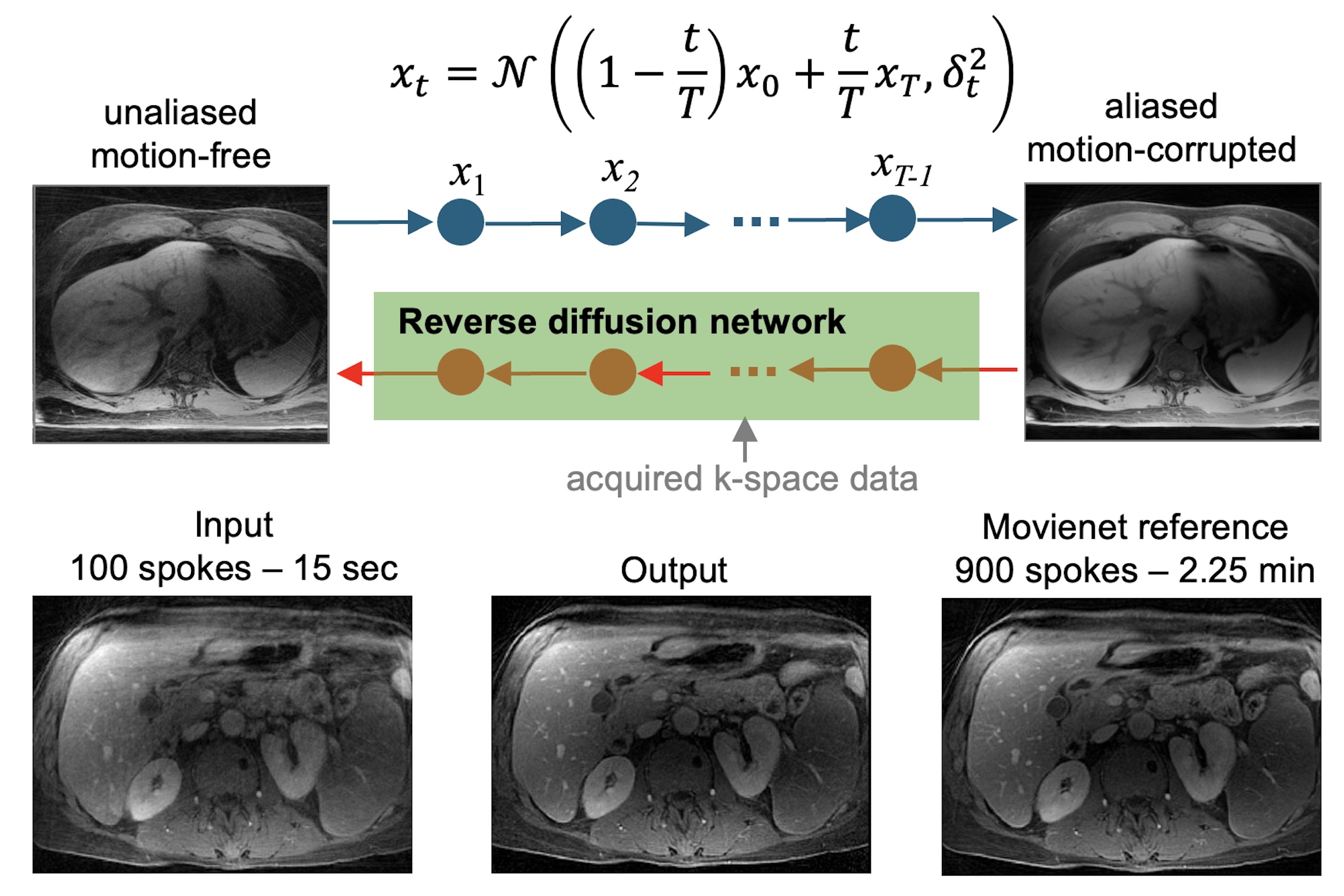
- Generative diffusion bridge-based reconstruction for acceleration motion-compensated abdominal MRI in less than 20 seconds: a diffusion bridge model enables to transform between the distribution of two types of images directly without converting images to noise and were able to highly accelerate and compensate for motion in abdominal MRI, as shown in Figure 4.